Rosetta
Analysis
CS329e Spring 07
Rosetta Stone
Protein
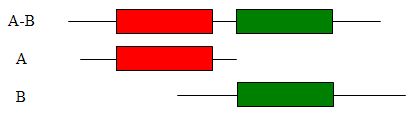
Two polypeptides A and B in one organism are likely to interact if their homologs are expressed as a single polypeptide AB in another. The latter polypeptide (AB) is called a Rosetta Stone protein, as it contains information about both A and B. Marcotte et al. [1] have proposed that fusion to form a single polypeptide reduces the entropy of dissociation of A and B. The result is a huge increase in the local concentration of A with respect to B.
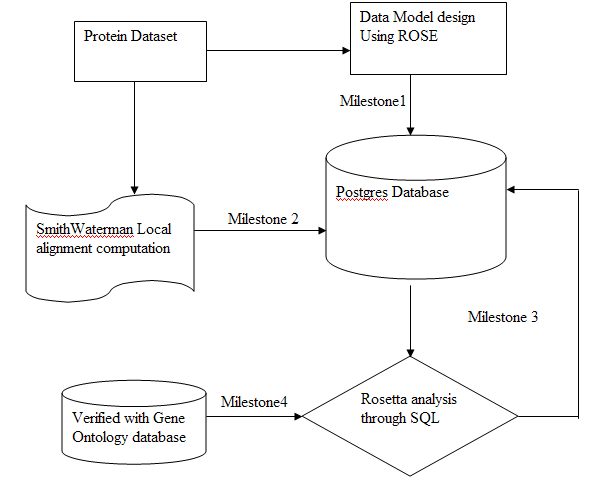
Project Overview
Results Demo (Milestone 5)
Search results by accession Number
Search results by gene product name
Search results by sequence
Search results by function
Predicate possible gene function.
…….
Reference:
Marcotte EM, Pellegrini M, Ng HL, Rice DW, Yeates TO, Eisenberg D: Detecting protein function and protein-protein interactions from genome sequences.
Science 1999, 285:751-753.
Dandekar T, Snel B, Huynen M, Bork P: Conservation of gene order: a fingerprint of proteins that physically interact.Trends Biochem Sci 1998, 23:324-328.
Rosetta Stone proteins: "chance and necessity"? Reiner A Veitia Genome Biology 2002, 3:interactions1001.1-1001.3