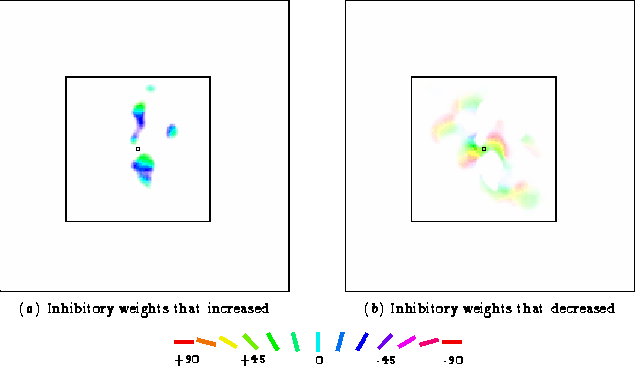
Adaptation has redistributed the inhibitory weights. Connections to neurons that have orientation preferences similar to the adaptation line became stronger (the blue areas in figure 5.4d). The strengthening results in the direct effect: inhibition for orientations close to the adaptation orientation is increased. However, since total weight strength for all inhibitory weights is constant (equation 3.4), the connections to other orientations (the yellow and red areas) must simultaneously decrease. This causes the indirect effect: inhibition for distant orientations is reduced. Chapter 6 discusses possible biological mechanisms for this weight normalization.
Since the changes for each neuron are relatively small, the difference
may not be readily apparent from figure 5.4.
Some changes are visible on close inspection in the central blue and
red-orange areas; compare figure 5.4 (
c) and (d). To highlight the changes,
figure 5.5 shows the result of
subtracting the weight plots from before and after adaptation.
 |