



One principle of DLM is that the links between two layers can be cleaned up and structured on the basis of correlations between pairs of neurons (see Figure 5 and Movie 1). The correlations result from the layer synchronization described in the previous section. The link dynamics typically consists of a growing term and a normalization term. The former lets the weights grow according to the correlation between the connected neurons. The latter prevents the links from growing infinitely and induces competition such that only one link per neuron survives which suppresses all others. The corresponding equations are (cf. Equations 6):

Links are initialized by the similarity  between the jets
between the jets
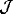 of connected nodes
[19].
of connected nodes
[19].
The parameter  guarantees a
minimal positive synaptic weight, permitting each link to suppress
others, even if the similarity between the connected neurons is
small. This can be useful to obtain a continuous mapping if a link
has a neighborhood of strong links inducing high correlations between
the pre- and postsynaptic neurons of the weak link. The synaptic
weights grow exponentially, controlled by the correlation between
connected neurons defined as the product of their activities
guarantees a
minimal positive synaptic weight, permitting each link to suppress
others, even if the similarity between the connected neurons is
small. This can be useful to obtain a continuous mapping if a link
has a neighborhood of strong links inducing high correlations between
the pre- and postsynaptic neurons of the weak link. The synaptic
weights grow exponentially, controlled by the correlation between
connected neurons defined as the product of their activities
 . The learning rate is
additionally controlled by
. The learning rate is
additionally controlled by  . Due to the
Heavyside-function
. Due to the
Heavyside-function  , normalization takes place only if links
grow beyond their initial value. Then, the link dynamics is
dominated by the normalization term, with a common negative
contribution for all links converging to the same neuron. Notice
that the growth term, based on the correlation, is different for
different links. Thus the link with the highest average correlation
will eventually suppress all others converging to the same neuron.
Since the similarities
, normalization takes place only if links
grow beyond their initial value. Then, the link dynamics is
dominated by the normalization term, with a common negative
contribution for all links converging to the same neuron. Notice
that the growth term, based on the correlation, is different for
different links. Thus the link with the highest average correlation
will eventually suppress all others converging to the same neuron.
Since the similarities  cannot be larger than 1, the
synaptic weights
cannot be larger than 1, the
synaptic weights  are restricted to the interval
are restricted to the interval 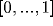 .
.

Figure 5: (click on the image to view a larger version) Connectivity and correlations
developing in time. It can be seen how the correlations develop
faster and are cleaner than the connectivity. Both are iteratively
refined on the basis of the other.
Movie 1: Connectivity and correlations developing in time as in Figure 5 (350 kB).


