 scale.common.Root
scale.common.Root
 scale.score.Note
scale.score.Note
 scale.score.chords.Chord
scale.score.chords.Chord
 scale.score.chords.SequentialChord
scale.score.chords.SequentialChord
 scale.score.chords.LoopTailChord
scale.score.chords.LoopTailChord
|
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||
java.lang.Objectscale.common.Root
scale.score.Note
scale.score.chords.Chord
scale.score.chords.SequentialChord
scale.score.chords.LoopTailChord
public class LoopTailChord
This class is used to collect the loop edges so that the loop header has two and only two in-coming CFG edges.
$Id: LoopTailChord.java,v 1.33 2007-10-04 19:58:23 burrill Exp $
Copyright 2007 by the
Scale Compiler Group,
Department of Computer Science
University of Massachusetts,
Amherst MA. 01003, USA
All Rights Reserved.
This class represents a non-action. No code is generated for this node.
We need to mark the end of a loop so that there are only two
in-coming CFG edges to a LoopHeaderChord
instance. For example, consider the following C code:
void tail(int k)
{
int i;
i = 0;
while (i++ < k) {
if (i == 2)
continue;
ftn(i);
}
}
We want to represent this as
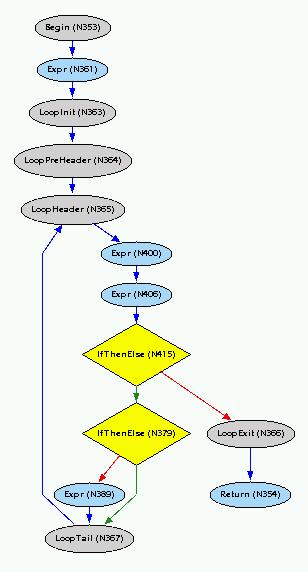
LoopHeaderChord,
LoopPreHeaderChord,
LoopExitChord,
LoopInitChord| Field Summary |
|---|
| Fields inherited from class scale.score.chords.Chord |
|---|
lineNumber |
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
LoopTailChord()
|
|
LoopTailChord(Chord next)
|
|
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
Chord |
copy()
Make a copy of this CFG node with the same out-going CFG edges. |
DColor |
getDisplayColorHint()
Return a String specifying the color to use for coloring this node in a graphical display. |
LoopHeaderChord |
getLoopHeader()
Return the LoopHeaderChord associated with this loop tail. |
boolean |
isLastInBasicBlock()
Return true if this is the last Chord in this Basic Block. |
boolean |
isLoopTail()
Return true if this CFG node is a LoopTailChord instance. |
boolean |
isSpecial()
Return true if this is chord was added for the convenience of the compiler and does not correspond to actual source code in the user program. |
void |
unlinkChord()
Break any un-needed links from a Chord that is being deleted. |
void |
visit(Predicate p)
Process a node by calling its associated routine. |
| Methods inherited from class scale.score.Note |
|---|
getChord, getEssentialUse, setAnnotationLevel, setReportLevel, toString, validate |
| Methods inherited from class scale.common.Root |
|---|
addAnnotation, allAnnotations, allMatchingAnnotations, getAnnotation, getDisplayName, getDisplayString, getNodeCount, getNodeID, hasAnnotation, hasEqualAnnotation, hashCode, removeAnnotation, removeAnnotations, toStringAnnotations, toStringClass, trace, trace, trace |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, notify, notifyAll, wait, wait, wait |
| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public LoopTailChord(Chord next)
public LoopTailChord()
| Method Detail |
|---|
public Chord copy()
Chord
copy in class Chordpublic LoopHeaderChord getLoopHeader()
getLoopHeader in class Chordpublic boolean isLastInBasicBlock()
isLastInBasicBlock in class SequentialChordChord.lastInBasicBlock(),
Chord.isFirstInBasicBlock(),
Chord.firstInBasicBlock()public boolean isSpecial()
isSpecial in class Chordpublic boolean isLoopTail()
LoopTailChord instance.
isLoopTail in class Chordpublic void unlinkChord()
unlinkChord in class Chordpublic void visit(Predicate p)
Note
Each class has a visit(Predicate p) method. For
example, in class ABC:
public void visit(Predicate p)
{
p.visitABC(this);
}
and the class that implements Predicate has a method
public void visitABC(Note n)
{
ABC a = (ABC) n;
...
}
Thus, the class that implements Predicate can call
n.visit(this);where
n is a Note sub-class without
determining which specific sub-class n is.
The visit pattern basically avoids implementing a large
switch statement or defining different methods
in each class for some purpose.
visit in class NotePredicatepublic DColor getDisplayColorHint()
getDisplayColorHint in interface DisplayNodegetDisplayColorHint in class ChordDColor
|
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||